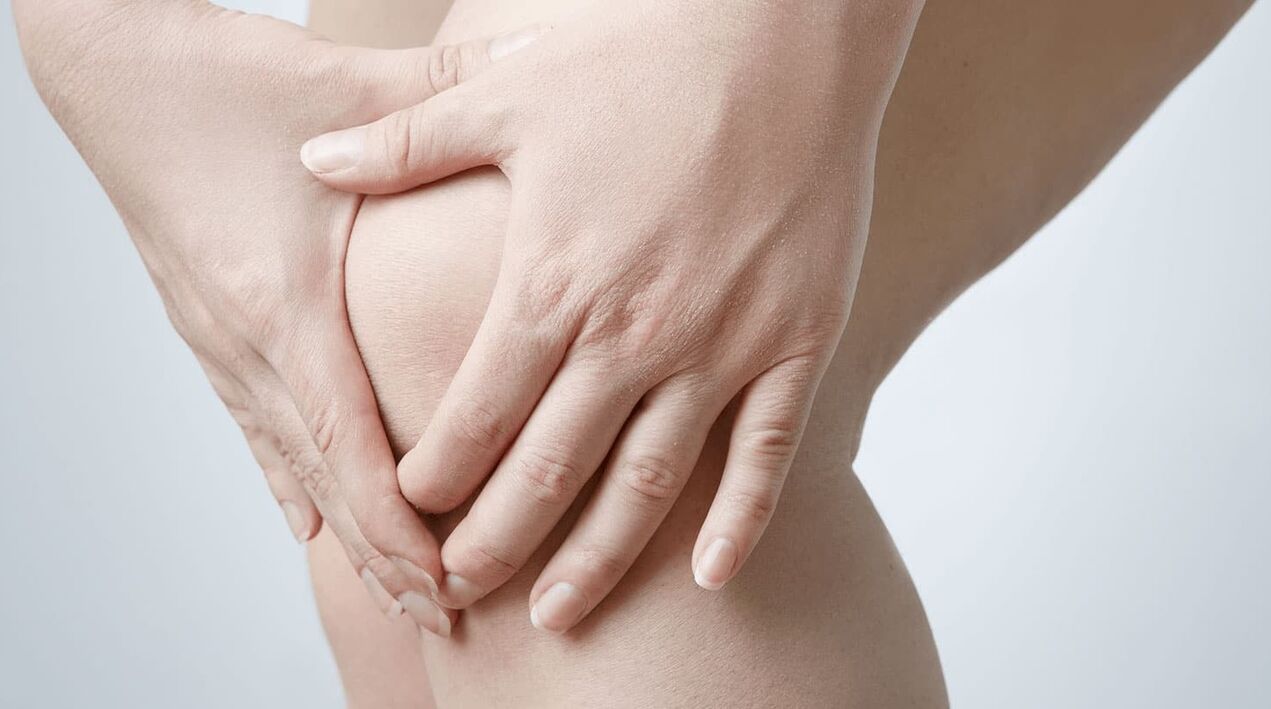
The knee joint is one of the most complex joints in the human body.Such “complicated” devices, combined with constant loads, make the joints very vulnerable.
In this regard, it is not surprising that throughout our lives, at least once, each of us has experienced pain in the knee – dull, aching, sharp, muffled or even unbearable.Sometimes unpleasant sensations bother people only when walking or bending and straightening the legs, in some cases - regularly.
The nature of pain in the knee joint, as well as the causes that cause it, can be very different;in this article we will try to understand in detail why the knee hurts, and what to do in this case.
Causes of knee pain
Pain in the knee joint can be caused by injury or be pathological.Sometimes this is a symptom of a serious illness, which can be determined by the nature of the sensations and a number of additional signs.
Among the most common reasons why knees hurt are the following:
- Knee joint arthritis is an inflammatory disease.This can be an independent pathology or a symptom or complication of another disease.
- Osteoarthritis of the knee joint is a degenerative process of destruction of articular tissue;over a long period of time, it causes deformation and eliminates joint mobility.
- Due to injury due to a very strong blow to the knee, impact with a hard object, or fall.In this case, the joint is badly damaged and bent unnaturally.
- Ligament Damage – Any activity that involves physical effort can cause knee injury.This often occurs during exercise and during active recreation, and sharp pain is immediately felt and the joint swells.If this occurs, any further pressure on the injured leg should be avoided until medical assistance is given, so as not to aggravate the injury.
- Meniscus damage.The meniscus is a round piece of cartilage in the knee joint that is easily damaged by squatting or twisting suddenly.Doctors diagnose this cause after conducting a direct examination, ultrasound and X-ray.
- Bursitis.Many people wonder why knees hurt when bent.There may be many answers to this question, but sometimes it is the usual formation of excess fluid in the joint, or more precisely in the bursa where it is located.The pain is not localized and often spreads to the surrounding area, even to the toes.Bursitis can manifest in an acute form, but often becomes chronic.Acute bursitis is expressed as sharp pain in the leg above the knee or in the knee itself, redness of the skin and significant limitation of leg mobility.Fluid accumulation can be easily felt even through the skin;the swelling has clear contours.
- Pain occurs when a cyst forms below the knee (Becker's cyst).Such formations appear in the fossa as a result of previously observed inflammatory processes in the knee joint.Substances accumulated during inflammation in the joint penetrate into the tendon area of the popliteal fossa and are localized in the deep part of the fossa.
- Tendonitis (inflammation of ligaments and tendons) is characterized by swelling and discomfort in certain areas.It is enhanced by flexion and extension of the knee and contraction of the muscles associated with the affected tendon, and spreads to neighboring muscles in the leg and thigh.
- Ischemic pain - occurs due to impaired blood supply to the knee joint.The cause may be sudden changes in weather, prolonged cold weather, and excessive physical activity.Usually, the pain is localized symmetrically, that is, in both knees, has the same intensity and does not affect joint mobility.
Acute or chronic knee pain that appears should not be ignored, so you need to consult a doctor.After completing the diagnosis, the specialist will tell you what to do in a particular case.Treatment may consist of tablets, ointments, liniments, physical procedures, and surgery.
Diagnostic
First, the orthopedist examines the patient's affected knee, performs movement tests and collects an anamnesis to make an accurate diagnosis.Additionally, the doctor may prescribe the following examinations:
- Instrumental - using radiography.Ultrasound, CT, MRI or densitometry.
- During laboratory examination, a general and biochemical examination is carried out, examination of smears and blood for bacterial microflora, serological examination, puncture of bone marrow and joint fluid.
- Invasive methods involve arthroscopy.
Based on the results of tests and examinations, the specialist makes a diagnosis and tells you how to treat knee pain in your case.
Knee pain treatment
The doctor can determine why the joint hurts.Therefore, a timely visit to a specialist is an important component for quickly and correctly eliminating the problem that has arisen.However, whatever the cause of knee pain, the first thing to do is reduce the load on the joints.Often during periods of acute pain, patients require bed rest followed by leg activation.It is recommended to use a cane or crutches when walking, and wear soft and comfortable shoes.In some cases, doctors prescribe orthopedic insoles.
At home, the main treatments for knee pain are chondroprotectives, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs.The form of release of this drug can be different (gel, cream, ointment, injection, tablet).Specialists prescribe one form of medication or another depending on the type, degree and location of damage.
- NSAIDs are most effective in relieving pain and inflammation.But these drugs have no effect on the cause of the disease.
- If your knee is swollen and painful, an ice pack will help.You can take an ice pack and apply it to the damaged area.After some time, the pain will start to subside.
- On the contrary, chondroprotectors do not reduce pain, but with long-term use they help to restore damaged cartilage tissue, restore joint function, and reduce the number of disease recurrences.
- Applying a support bandage may also help.But you must be sure that this can be done to treat your injury, otherwise you will only make things worse.
- If your knees hurt when sitting in one place for a long time, then you need to move around a little.A sedentary lifestyle or sedentary work is very dangerous - there is a risk of gaining excess weight, which will put pressure on the knee joints, and it is also very dangerous that all the time without moving, the knees stagnate.
Drug treatment is usually complemented by a physiotherapy program.This allows you to quickly relieve pain, shorten treatment, and reduce the dose of drugs.
It is equally important to follow a diet - consuming plant foods rich in vitamins, fish dishes and seafood helps to restore articular cartilage.And of course, when the pain can be overcome, we must try to prevent the pain from returning: live a healthy lifestyle, strengthen the body and not create excessive stress.